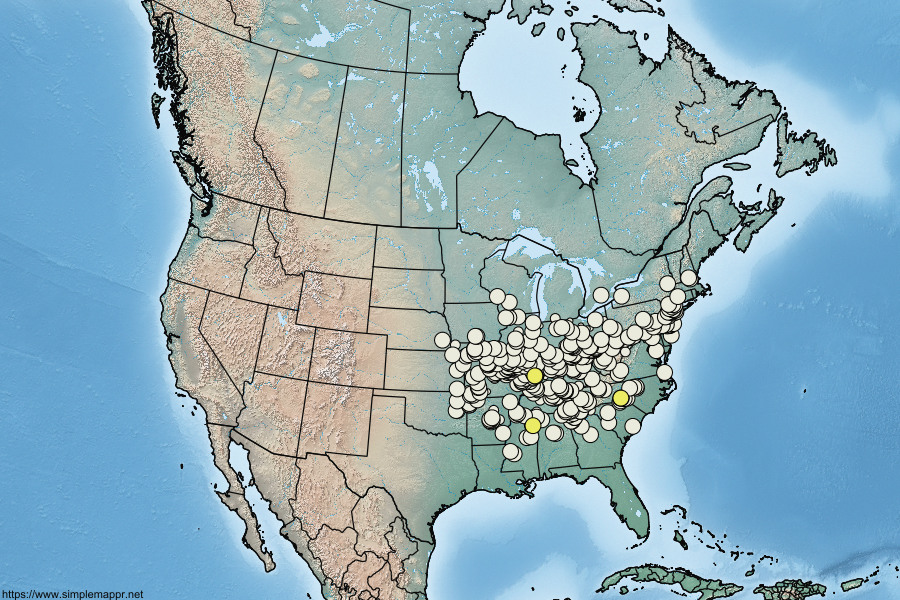
 Catocala angusi
Catocala angusi
Grote, 1876
The 7 Juglandaceae-feeding Catocala species
angusi,
habilis,
judith,
obscura,
residua,
robinsonii and
serena are all
Shagbark Hickory (Carya ovata) specialists that hide under shags rather than on
branches and twigs, are correspondingly dorso-laterally flattened with suffused/reduced ventral
spotting on A1-A4 and A7-A8, lack lateral filaments, and often sport darker lateral (cf. dorsal) "racing stripes."
Larvae of
obscura
and
residua
not reliably separable from one another without rearing to adult, but as a pair, differ from the other
5 in having mostly lighter grey ground color, coupled with head capsule with black markings
limited to the mandibular and ocellar areas and absent from the lobes/vertices, and ventral spotting
usually present.
Larvae of
serena
lacking ventral spotting or nearly so (but some
angusi and
habilis indistinguishable on
this character),
usually with somewhat darker ground color than obscura/residua, head
capsule as in obscura/residua but with black markings
noticeably broader.
Larvae of
judith like
serena though usually darker ground color still, and with ventral spotting present.
Larvae of
robinsonii
with ground color and ventral spotting usually like obscura/residua, but head capsule thoroughly overtaken by
broad black mandibular and lateral bands, often extending/framing over the vertices, and central area
of lobes often demaculated of pattern.
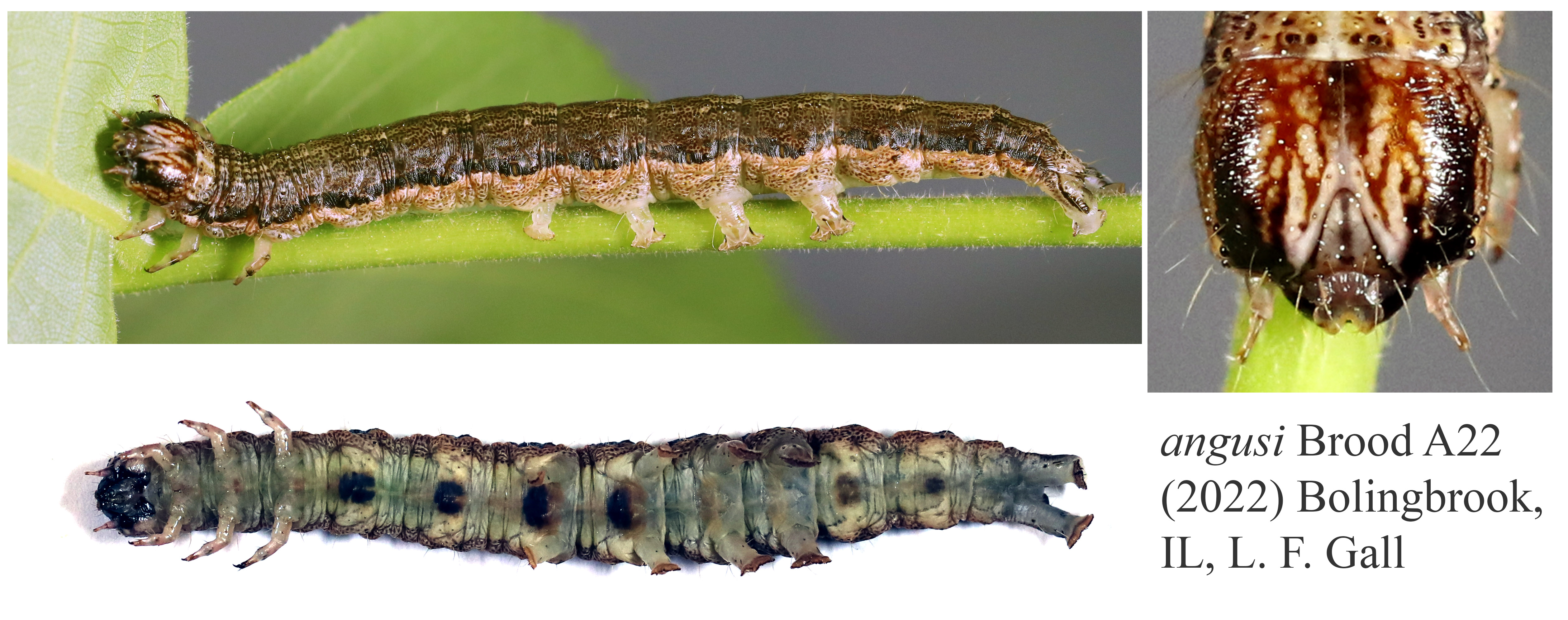
Larvae of
angusi and
habilis like
robinsonii although
usually with darker ground color, head capsule somewhat less overtaken with black especially laterally, and variable
ventral spotting (present to mostly absent).
Both head capsule and body of
habilis
characteristically "glassy" although some
angusi similar.
Larvae of these 7 species tend to have extensive black ventrally on head capsule lobes, labrum, maxilla and/or
prothoracic gland (some serena, angusi, habilis particularly so).
Statements in Wagner et al. (2011) about larval separability among these 7 species are mostly overly optimistic,
since the range of character variation is greater than previously understood.




|